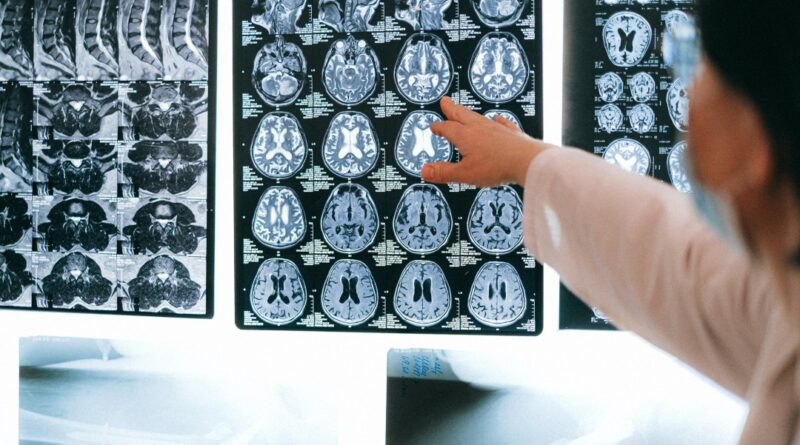
EHRs Play Critical Role in Radiology Decision-Making
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have revolutionized the healthcare industry, impacting various medical specialties, including radiology. Radiology, the branch of medicine that uses medical imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases, has seen significant advancements in decision-making processes due to the integration of EHRs.
The pivotal role AdvancedMD EHR plays in radiology decision-making, emphasizing their impact on patient care, efficiency, and data-driven insights.
I. Enhanced Data Accessibility and Patient Information:
One of the primary advantages of EHRs in radiology is the immediate access to comprehensive patient information. Radiologists can access a patient’s medical history, laboratory results, medication lists, and clinical notes within the EHR system.
This wealth of information aids radiologists in making informed decisions about the appropriateness of imaging studies, interpreting images accurately, and recommending appropriate follow-up procedures.
A. Improved Clinical Context:
EHRs provide radiologists with a contextual understanding of a patient’s condition. This allows for more accurate interpretation of radiological findings, reducing the likelihood of misdiagnoses and unnecessary tests. For instance, knowing a patient’s medical history, allergies, or prior imaging studies can influence the interpretation of a current scan.
B. Seamless Communication:
EHRs facilitate seamless communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals. Radiologists can easily consult with referring physicians, specialists, and other members of the healthcare team by sharing electronic records and discussing patient cases within the EHR system. This real-time collaboration contributes to better decision-making and patient care.
II. Enhanced Imaging Workflow and Efficiency:
EHRs streamline radiology workflows, making the entire process more efficient. They eliminate the need for paper-based records and reduce the time spent on administrative tasks, allowing radiologists to focus more on clinical decisions and patient interactions.
A. Order Management:
EHRs enable automated order management, ensuring that radiology requests are accurate and complete. This reduces errors and enhances the efficiency of the imaging process, leading to faster diagnoses and treatment decisions.
B. Image Integration:
Integration with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) allows radiologists to access and interpret images seamlessly within the EHR interface. This integration speeds up the reporting process, as radiologists can view images and immediately incorporate findings into patient records.
C. Voice Recognition Technology:
EHRs often integrate voice recognition technology, allowing radiologists to dictate their interpretations directly into the electronic record. This not only improves documentation accuracy but also accelerates the reporting process.
III. Data Analytics and Decision Support:
EHRs in radiology go beyond storing patient data; they also provide powerful analytical tools and decision support systems. These tools help radiologists make data-driven decisions, particularly in complex cases.
A. Predictive Analytics:
EHRs can analyze vast datasets to identify trends and patterns in radiological findings. Radiologists can leverage this information to anticipate disease progression, identify high-risk patients, and tailor treatment plans accordingly.
B. Clinical Decision Support:
EHRs offer clinical decision support systems that provide radiologists with evidence-based guidelines, best practices, and alerts. These tools aid in making more informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
IV. Quality Improvement and Reporting:
EHRs play a vital role in quality improvement initiatives within radiology. They facilitate outcome tracking, benchmarking, and reporting, enabling radiologists to continually assess and enhance the quality of their services.
A. Performance Metrics:
EHRs allow radiologists to track key performance metrics, such as report turnaround times, diagnostic accuracy rates, and utilization of imaging resources. This data-driven approach helps identify areas for improvement and optimization.
B. Compliance and Accreditation:
Radiology practices can use EHR data to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and accreditation standards. Meeting these standards is essential for maintaining the highest quality of care.
Conclusion:
Electronic Health Records have significantly transformed radiology decision-making processes. They empower radiologists with immediate access to patient data, enhance workflow efficiency, provide data analytics capabilities, and support quality improvement initiatives.
As a result, EHRs not only improve patient care through more accurate diagnoses and better-informed treatment decisions but also contribute to the overall advancement of the field of radiology. The integration of EHRs into radiology practice is not merely a technological advancement; it is a critical driver of improved healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
Patient engagement software tailored to radiology not only benefits patients by improving their experience but also contributes to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of radiology departments and imaging centers. It enhances communication, reduces administrative burdens, and empowers patients to take an active role in their healthcare, ultimately leading to better outcomes and patient satisfaction.